Diesel vs. Natural Gas Generators: Key Differences and Use Cases
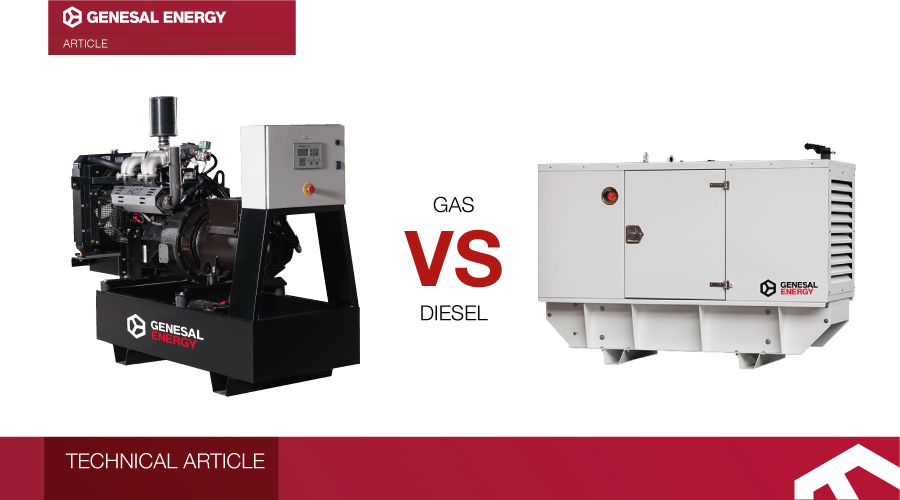
The two most common generator types on the market are diesel engine powered generators and those using gas powered engines.
Apart from the fuel powering them, they have other distinctive qualities which make them more or less adequate according to the use we want to give them.
Let’s see what they are.
Note: In this article, “gas” refers to natural gas or liquefied petroleum gas (LPG), not gasoline (petrol). These are commonly used in gas-powered generators, not to be confused with petrol-fueled engines.
Diesel generators
The reliability of a classic
For quite a long time, diesel engine generators have been a standard in the market. Their good reputation was the result of a great flexibility of application, both in industrial and household areas, as well as their robustness and reliability.
This type of generator may be used as a main power supply, as well as for co-generation or emergency applications. They are fully autonomous and may, therefore, function in places which have absolutely no power-supplying networks.
What advantages have made diesel generators so popular?
- They are more easily disassembled and installed than gas units, making their installation wherever needed a simpler task, while also using a fuel which is easily accessible and more economical than gasoline.
- They are robust and sustainable, capable of ensuring many hours of yearly operation.
- Diesel fuel gives high efficiency to the equipment using it because it burns at a much higher temperature than gasoline.
- Diesel fuel is also very safe because it is less flammable than other types of fuel.
The main disadvantage of this type of generator, as in the case of any machinery which includes a diesel engine, is that it causes high levels of polluting gas emissions. Therefore, the present day diesel generators incorporate an additional antiparticle filtration system that ensures its conformity with the legislation in force.
Natural gas powered generators
Clean and economical energy
Gas engine generators have gained much popularity due to their great reliability, cost efficiency and sustainability.
This type of generator can be used as a primary power source, in co-generation applications or as an emergency source and its engine may be fuelled by liquefied natural gas (LNG) or liquefied petroleum gas (LPG). The latter is a gaseous fuel obtained from the distillation of oil.
Generators powered by LNG fuelled engines get their fuel from the natural gas distribution network, whereas LPG fuelled generators are connected to a tank which will have to be periodically refuelled.
What are the benefits of natural gas powered generators?
- They are more respectful of the environment, because the gas causes less emission than other non-renewable fuels (such as coal, diesel or gasoline).
- They are economical, because gas is the most affordable fuel, second only to coal (which is not an option due to its high emission level).
- They are high-efficiency generators in co-generation applications.
- When fuelled by an underground natural gas network, the fuel supply is not conditioned by inclement weather or problems with the communication infrastructure (which do condition diesel generators that need periodic refuelling).
- They are highly compatible and easy-to-use units, given that it is possible to install them in remote locations, using high capacity tanks.
- They are very quiet generators.
Among the disadvantages of this type of generator, one must consider the following:
- Liquefied natural gas (LNG) powered generators are less autonomous than diesel engine ones because it is absolutely necessary to connect them to a distribution network.
- In the case of LNG equipment connected to the network, one has to take into account that any catastrophe or natural disaster can affect the supply system.
- Gas is an exceptionally flammable fuel and entails a bigger fire hazard than diesel.
- The engine and control system are much more demanding, which can result in the product’s final price being higher.
- They require a more punctual and complex maintenance.
Diesel vs Gas Generators: Which One Should You Choose?
Deciding between a diesel or gas-powered generator requires careful consideration of various factors. Each type has its own set of advantages and disadvantages that make them suitable for different applications and environments. Here are the key factors to consider:
1. Application and Usage
- Primary Power Source: If you need a generator for continuous operation, such as in remote locations without a power grid, diesel generators are often preferred due to their robustness and fuel efficiency.
- Emergency Backup: Both diesel and gas generators can serve as reliable backup power sources. However, gas generators, especially those connected to a natural gas line, can provide uninterrupted fuel supply during emergencies without the need for refueling.
2. Environmental Impact
- Emissions: Gas generators produce fewer emissions compared to diesel generators, making them a more environmentally friendly option. This can be a critical factor if you are concerned about meeting stringent environmental regulations or minimizing your carbon footprint.
- Noise Levels: Gas generators are generally quieter than diesel generators, which can be important in residential areas or locations where noise pollution is a concern.
3. Fuel Availability and Cost
- Fuel Costs: Diesel fuel is typically more expensive than natural gas, but it provides higher energy efficiency, which can offset the cost over time.
- Fuel Supply: Gas generators connected to a natural gas line have a continuous fuel supply, whereas diesel generators require regular refueling. However, in areas without natural gas infrastructure, diesel may be the more practical choice.
4. Maintenance and Longevity
- Maintenance Requirements: Diesel generators are known for their durability and lower maintenance needs. Gas generators, while efficient, often require more frequent and complex maintenance due to the nature of the fuel and engine.
- Lifespan: Diesel generators tend to have a longer operational lifespan, making them a more cost-effective option in the long run for high-demand applications.
5. Safety Considerations
- Flammability: Natural gas is highly flammable, posing a greater fire hazard compared to diesel. Diesel fuel, being less volatile, is considered safer to store and handle.
- Reliability: In situations where natural disasters might disrupt gas supply lines, diesel generators offer greater reliability as they can operate independently of external fuel supply networks.
What About Gasoline Generators?
In some markets, especially in North America, “gas-powered generator” often refers to gasoline-fueled engines. While these are common for small portable generators, this article focuses on natural gas and LPG-powered equipment, typically used in industrial and backup applications.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is the difference between a diesel and a natural gas generator?
Diesel generators run on diesel fuel and are known for their durability, fuel efficiency, and high performance in demanding environments. Natural gas generators use either piped natural gas (LNG) or liquefied petroleum gas (LPG), offering lower emissions and quieter operation.
2. Which generator is more efficient, diesel or natural gas?
Diesel generators are typically more fuel-efficient and better suited for continuous use or high-load applications. However, natural gas generators may offer better cost efficiency in areas with existing gas infrastructure.
3. Are natural gas generators more environmentally friendly than diesel?
Yes. Natural gas generators produce significantly fewer emissions, including NOx and particulate matter, making them a more environmentally friendly choice compared to diesel generators.
4. Can a natural gas generator run during a power outage?
Yes, especially if it’s connected to a natural gas grid. These generators can provide uninterrupted fuel supply during emergencies without the need for manual refueling—unlike diesel units.
5. What are the maintenance differences between diesel and gas generators?
Diesel generators require less frequent maintenance and are generally easier to service. Gas generators may require more specialized maintenance due to their fuel system and engine complexity.
6. Which type of generator lasts longer?
Diesel generators usually have a longer lifespan thanks to their robust design and lower engine RPMs. They’re ideal for intensive use and long-term reliability.
Conclusion
Choosing the right generator depends on your specific needs and circumstances. At Genesal Energy, we understand that every project is unique. Our experts are here to help you assess your requirements and recommend the best solution tailored to your needs. Whether you prioritize environmental impact, fuel efficiency, or operational reliability, we provide comprehensive guidance to ensure you make an informed decision.
For personalized advice and more information, please contact us at:
consultas@genesal.com +34 900 730 124










